
The mask does not need to match your local subnet mask since it is used to define the range.
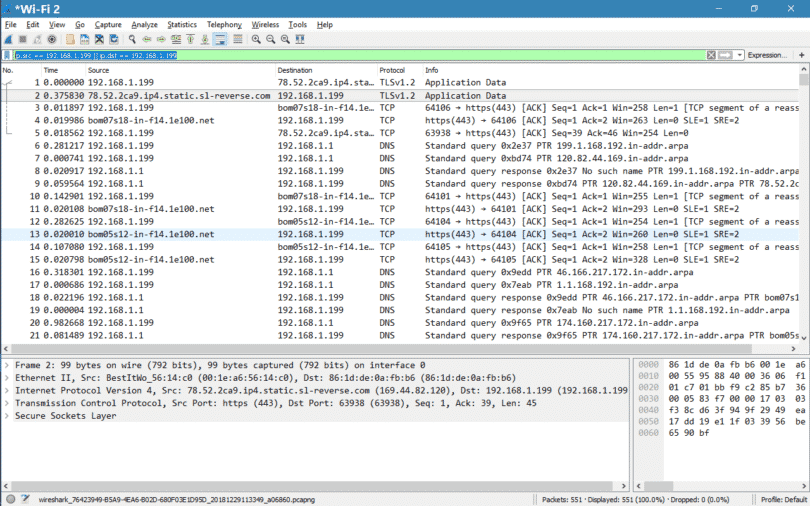
To check if promiscuous mode is enabled, click Capture > Options and verify the “Enable promiscuous mode on all interfaces” checkbox is activated at the bottom of this window. You can also limit the filter to only part of the ip address. You can simply use that format with the ip.addr or ip.addr eq display filter. If you have promiscuous mode enabled-it’s enabled by default-you’ll also see all the other packets on the network instead of only packets addressed to your network adapter. Wireshark captures each packet sent to or from your system. You can configure advanced features by clicking Capture > Options, but this isn’t necessary for now.Īs soon as you click the interface’s name, you’ll see the packets start to appear in real time. For example, if you want to capture traffic on your wireless network, click your wireless interface. Capturing PacketsĪfter downloading and installing Wireshark, you can launch it and double-click the name of a network interface under Capture to start capturing packets on that interface. Don’t use this tool at work unless you have permission. = 1 and a quick warning: Many organizations don’t allow Wireshark and similar tools on their networks. =1 or (tcp.seq=1 and tcp.ack=1 and tcp.len=0 and _rtt) Find files by typeįrame contains “(attachment|tar|exe|zip|pdf)” Find traffic based on keywordįrame contains facebook Detecting SYN Floods Http.request or http.response Filter three way handshake Http.request Filter all http get requests and responses Tcp.port = 80 & ip.addr = 192.168.0.1 Filter all http get requests !(arp or icmp or dns) Filter IP address and port !er_agent contains || !er_agent contains Chrome Filter broadcast traffic Tcp.srcport = 80 Filter TCP port destination The mask does not need to match your local subnet mask since it. You can simply use that format with the ip.addr or ip.addr eq display filter. Ip.addr = 192.168.0.1/24 and ip.addr = 192.168.1.1/24 Display traffic between two specific workstations This is where the subnet/mask option comes in. !ip.addr =192.168.0.1 Display traffic between two specific subnet
#Wireshark filter ip.address mac
To get the mac address, type ncpa. Icmp Exclude IP address: remove traffic from and to IP address To filter out a mac address in Wireshark, make a filter like so: not eth.addrF4-6D-04-E5-0B-0D. Ip.addr = 192.168.0.1/24 Filter by protocol: filter traffic by protocol name Ip.dst = 192.168.0.1 Filter by IP subnet: display traffic from subnet, be it source or destination Ip.src = 192.168.0.1 Filter by destination: display traffic only form IP destination Wireshark and TShark share a powerful filter engine that helps remove the noise from a packet trace and lets you see only the packets that interest you. Ip.addr = 192.168.1.1 Filter by source address: display traffic only from IP source (Ideally, the Wireshark display filter validation could be improved to detect this and turn the expression red instead of green.) ip.address 153.11.105.34 or 153.11.105.35 This is invalid because there is no field called 'ip.address' and you need to specify the field name for the second IP address too. Filter by IP address: displays all traffic from IP, be it source or destination Bellow is a list of the most common type of filtering. The filtering capabilities are very powerful and complex, there are so many fields, operators and options and their combination becomes overwhelming. Fortunately, wireshark has display filters so that we can search for specific traffic or filter out unwanted traffic, so that our task becomes easier. Wireshark takes so much information when taking a packet capture that it can be difficult to find the information needed.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
